自然
宗像の川
釣川とは
釣川は宮若市との境、宗像市吉留の山林中にその源を発し、朝町川・八並川・山田川などの支流と合流しながら市内を東西に流れ、しだいに北へと流れを変えて樽見川と合流、江口において玄界灘へとそそぐ延長が約16km、流域面積が約99km²の二級河川です。
宗像地方にヒトが住み始めたのは今から約3万年~約1万年前の後期旧石器時代と呼ばれる時代で、その後の縄文時代(約1万年前~約2,300年前まで)の遺跡がいくつか発見されています。縄文時代には釣川にそって海が内陸まで入り込み、その周辺をうっそうとしたカシやシイなどの森林がおおっていたと考えられています。
弥生時代(約2,300年前~約1,700年前まで)になると内陸深く入り込んでいた海は退き、釣川沿いには肥沃な平野が広がり、稲が作られ、たくさんの人が定住するようになり、ムラをつくるようになりました。以来、古墳時代(3世紀末~7世紀半ばまで)から、つい数十年前まで、釣川は重要な農業用水源として大切に守られ、また治水・利水のために、さまざまな河川改修の工事も行われてきました。

釣川をとりまく環境
宗像市のほぼ中央に広がる釣川水系は、この地域を取り囲む200~500mの分水嶺(ぶんすいれい※1)によって隣接する他の地域の水系から区分され独立した水系をなしています。

|
番号
|
名前 (よみ)
|
|---|---|
| 1 | あみだ川(あみだがわ) |
| 2 | 新川(しんかわ) |
| 3 | 牟田川(むたがわ) |
| 4 | 田野川(たのかわ) |
| 5 | 諸見川(もろみがわ) |
| 6 | 前川(まえかわ) |
| 7 | 樽見川(たるみがわ) |
| 8 | 梛野川(なぎのがわ) |
| 9 | 阿久住川(あくずみがわ) |
| 10 | 吉田川(よしだがわ) |
|
番号
|
名前 (よみ)
|
|---|---|
| 11 | 横山川(よこやまがわ) |
| 12 | 四十里川(しじゅうりがわ) |
| 13 | 大井川(おおいがわ) |
| 14 | 用山川(もちやまがわ) |
| 15 | 八並川(やつなみかわ) |
| 16 | 山田川(やまだかわ) |
| 17 | 朝町川(あさまちがわ) |
| 18 | 松本川(まつもとがわ) |
| 19 | 釈迦院川(しゃかいんがわ) |
| 20 | 高瀬川(たかせがわ) |
|
番号
|
名前 (よみ)
|
|---|---|
| 21 | 古森川(こもりかわ) |
| 22 | 子下し川(こくだしがわ) |
| 23 | 綿打川(わたうちがわ) |
| 24 | 中山川(なかやまがわ) |
| 25 | 荒堀川(あらほりがわ) |
| 26 | 名残川(なごりがわ) |
| 27 | 久戸川(ひさとがわ) |
| 28 | 宮川(みやかわ) |
| 29 | 猿田川(さるたがわ) |
| 30 | 平山川(ひらやまがわ) |
宗像市吉留の山地を源流とする本流は、約16kmの流程を下り、玄界灘に流れ込みます。本流の両側の山地に源して、途中で合流する支流やそれらの2次支流は朝町川、高瀬川、八並川、山田川、横山川、樽見川等たくさんありますが、いずれも延長距離が本流の半分を超えません。流域面積も99k㎡程度で水系全体の規模は大きくありません。
※1分水界になっている山脈。雨水を異なった水系に分かつ山の峰々。分水山脈。
低地の多い釣川流域
釣川は、河川の長さに比べると流域面積が大きく、下流部では丘陵が張り出していて、宗像大社付近などに狭窄部(きょうさくぶ※1)を形作っています。
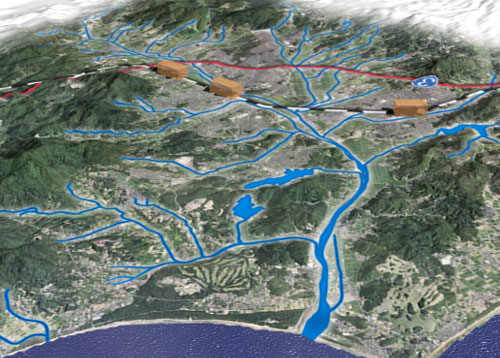
釣川の勾配は上流部を除くときわめて緩く、下流の東郷付近で数本の支流がまとまって本流と合流しています。このため釣川は、集中的な豪雨があれば、水が狭窄部や合流部付近にたまりやすく、広く氾濫しやすくなっています。釣川平野の低地部は、自然堤防状の微起伏が見られず、きわめて低く平らな状態です。これは、氾濫すると一面に水が溢れ、冠水と土砂堆積を繰り返してきたためといわれています。
昭和28年6月28日の集中豪雨では釣川沿岸でも氾濫し、鹿児島本線も不通になりました。
※1 狭くすぼまっていること。
むなかたの水事情
宗像市は、平成15年の旧宗像市と玄海町との合併、平成17年の大島村との合併を経て現在の「かたち」になりました。
宗像市では昭和30年代に始まる高度経済成長にともない、昭和36年に鹿児島本線が電化され、また、今日の住宅都市としての基礎となった「自由ヶ丘」や「日の里」の大型団地の開発が始まり人口が急増してきました。

それとともに生活で使う水の量も増加し、釣川の水を生活用水として利用するために「大井ダム」そして「吉田・多礼ダム」が造られましたが、流域面積が小さく流量は少ないことと、河川の途中にはたくさんの農業用井堰が作られていて、毎年5月中旬から10月中旬までは堰きとめられ農業用水として利用されることから、大井ダム(貯水池)への水のくみ上げはこれ以外の時期に限られていました。(北九州市からの受水により、平成23年度から大井ダムは上水道に利用されていません。)
また、ダムへの取水口は終末処理場の処理水の排水口より下流にありますので、宗像市では水道水もリサイクルしているのです。
人口の増加・都市化にともなってしだいに川の汚染が進みますが、公共下水道の整備にともない、生活排水による汚染は減少しています。また、道路の舗装化や河川の三面張りなどで雨水の地下浸透が妨げられるとともに、荒竹林化が目立つなどの森林の荒廃が進み、水源涵養機能が低下し、地下水の減少も進んでいます。
釣川の水は米や野菜を作る農業用水として、あるいは私たちの大切な飲料水として利用されていますが、決して昔のようなきれいな水ではなくなってしまいました。私たちは今こそ川の大切さをあらためて見直し、川をそして縁を守り、親しむことを考えていかなければなりません。
私たちにできること
今、私たちの日常生活から排出される生活排水で河川が汚れています。
みんなが飲んでいる水道水の大部分が川の水を使っています。ちょっとした心づかいでできる川をきれいにする方法をあげてみました。

使用前に洗剤の特性を知り、上手に使いましょう。

肥料としても有効です。


ドライブや行楽地でのゴミは持ち帰りましょう。
むなかた「水と緑の会」の
行っていること
むなかた「水と緑の会」は1991年11月30日設立され、釣川はもちろん宗像の自然と私たちの生活環境を守るため、さまざまな活動を行政と力を合わせて計画・実施しています。「水と緑の会」にはだれでも入会でき、会の活動は市の広報紙などでも紹介していますので、気軽に参加してください。
① 調査・研究事業
釣川の水質調査や生物の分布調査、水の浄化、景観の研究、水源涵養林の育成など専門家や先生を中心に、宗像の自然・生活環境保全のための調査・研究を行っています。
② 活動事業
宗像の自然・生活環境を保全するための具体的な活動を展開します。ひとりひとりの力を集結することが大切です。会員をはじめ一人でも多くの市民の参加をお願いします。具体的には、食廃油利用の石けん作りやホタル分布の調査とホタル養殖・飼育・放流、クリーン作戦(空缶、ゴミ拾い)等を行っています。
③ 広報・教育事業
宗像市のミニ環境講座などで、講演会や学習会を開催していますので、要望があれば申し込んでください。

福岡県や宗像市が
おこなっていること
① 河川改修
洪水から私たちの命や財産を守ることは何より大切なことです。そのために堤防・護岸工事などの河川改修工事がなされてきました。しかし、これらの工事によってそこにすむ生物たちのすみかが奪われてしまいました。そこで、相在では魚道やホタル護岸、漁巣ブロックといった生物たちのことも考えた工事がなされるようになりました。
② 下水道の整備
昔は川にたれ流しになっていた家庭排水を、下水道を整備することによって集め、きれいな水にして川に放流します。しかし、家庭でさまざま化学物質が使われるようになり、今までの下水道の設備では処理しきれず、危険な物質が含まれたまま放流されることも考えられます。
③ 水質の監視・調査
川を汚さないように監視したり、定期的に水質を調査したりしています。
④ 市民への広報・啓発活動
いろいろな機会に広報紙やチラシなどを使って市民へのPR、啓発活動を行っています。
⑤ 水辺の利用
市民が釣川に親しみ、釣川を憩いの場として利用できるように河畔公園の整備等を行ってきました。
⑥ 水源涵養林の育成
地下水や河川水を確保するために、福岡県の森林環境税を活用し、荒廃森林再生事業を行ったり、森林組合と協力したりして、山の緑を大切に守っています。
⑦ 美化活動
市民やボランティア団体と協力し、土手の草刈りやゴミ拾いなど行います。
 はじめに
はじめに お問い合わせ
お問い合わせ